Generative AI - from talk to action
18.08.2024 | 6 min ReadCategory: Artificial Intelligence | Tags: #Podcast, #AI
Generative AI has become a hot topic in the technology and data field. We are tired of idle chatter about the subject, and here we offer some experience-based advice on how you can go from theory to practice - fast!
What is generative AI?
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can produce new data resembling what they were trained on. Generative AI is used in many applications, such as image and video production, text generation, and in creative tools that can assist with design and content development. This field combines machine learning, statistics and often complex algorithms to create results that are difficult to distinguish from real, human-created content.
The main difference between generative and other forms of AI is that the purpose is to generate new content based on existing data, while other AI typically classifies or finds patterns in existing data.
| Type of AI | Purpose | Process | Examples | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generative AI | Create new content | Generates data and is evaluated by another model | GANs, VAEs | Image/video generation, text writing, music |
| Discriminative AI | Classify or recognise existing data | Learns to distinguish between different types of data | CNNs, RNNs, SVMs | Image/speech recognition, medical diagnostics, spam filtering |
| Reinforcement Learning (RL) | Learn to make decisions through trial and error | Updates actions based on rewards | Q-learning, DQN, Policy Gradient Methods | Games (such as AlphaGo), robotics, autonomous driving |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Understand and generate human language | Analyses and generates language based on patterns in data | BERT, GPT, Seq2Seq | Machine translation, chatbots, sentiment analysis |
| Computer Vision | Analyse and interpret visual data | Applies algorithms to understand images and videos | YOLO, Faster R-CNN, U-Net | Facial recognition, medical image analysis, self-driving cars |
| Recommendation Systems | Recommend products or content | Analyses user data to provide recommendations | Matrix Factorization, Collaborative Filtering, Content-Based Filtering | E-commerce, streaming services, social media |
| Anomaly Detection | Identify unusual patterns | Uses models to find deviations in data | Isolation Forest, One-Class SVM, Autoencoders | Fraud detection, quality control, network security |
| Speech Recognition | Convert speech audio to text | Applies models to transcribe speech | HMMs, Deep Speech, Wav2Vec | Digital assistants, dictation software, customer service |
Our use of generative AI
Glitni and our partner Telum have extensive experience with the use of generative AI, especially language models. Below, we distinguish between different uses of generative AI, from pre-packaged to fully customised, and provide examples of our use of generative AI.
Using language models in ready-made applications
Most applications will eventually get features that utilise generative AI. We work extensively with coding and programming, where generative AI has proven to be particularly useful.
Tools like GitHub Copilot can increase efficiency considerably. A common approach is to write comments or docstrings in the code, which GitHub Copilot then uses to suggest code. Often these suggestions are very good, and by pressing the tab key, the developer can quickly integrate them into the code. This can both increase the speed and improve the quality of the code produced.
In addition to GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT can be used for debugging and as support when you are unsure where to start with a task. With the new Copilot chat in VS Code, developers can now get help directly in the code interface, which further streamlines the workflow.
Using language models out of the box - e.g. ChatGPT
Generative AI can be used to structure work and prepare content. For example, you can use ChatGPT to create structures for projects or episodes based on the target audience and desired length. Although the results sometimes need to be adjusted slightly, the AI can provide a good starting point.
Once you have completed a project, AI can also be used to transcribe and clean up the content. This is particularly useful when it is necessary to make the transcription more readable and relevant, especially when slang or dialect is used.
Increased efficiency with custom GPTs and larger context windows
One of the keys to getting the most out of generative AI is to create custom GPTs for specific tasks. By investing time in pre-filling information into the context window, you can achieve much better assistance from the AI. The more information the AI receives, the better results it can deliver.
For example, if you ask for a tomato soup recipe, the AI needs to know your budget and preferences to give a good result. This principle applies to all types of AI use. Giving the AI the right context and information is crucial for achieving good results.
Going further: language models in your own solutions
To truly get impact from language models, it may in some cases require adaptations to existing processes and applications.
Language models can, for example, be used to index product images and videos. Using models like Instruct Blip, you can describe products in images and transcribe videos to index what is being said. This makes searches more effective and provides robust results regardless of language and spelling errors.
By using language models in both indexing and search, you can achieve robust results. This is not necessarily RAG (retrieval augmented generation), but vector-based search that makes it easier to find relevant content.
How should you approach generative AI?
Start with narrow use cases
Automating and streamlining processes and products with generative AI is not just about incremental improvements, but also about investing purposefully in use cases that can truly make a difference for your business. It will be important to think long-term about how to collect the data the AI needs.
But to bring it down a notch — start small. Maturity comes through practice. For businesses, it is important to start with narrow use cases where the information needed to solve the problem already exists.
Examples of narrow use cases
Here are examples of relatively narrow use cases where generative AI can significantly increase productivity:
- document analysis of e.g. legal documents
- transcription of video and audio in meetings
- image indexing
- self-service customer support
- content creation in marketing
- translation between languages
- programming
Remember that generative AI only plays a minor role in a larger process
Generative AI typically only plays a role in a larger process. Sometimes the role is small, other times it may be the step that enables the entire process to be automated. And when we can get there — that is when we can often save a great deal of time or dramatically increase quality.
Here is an example of such a process:
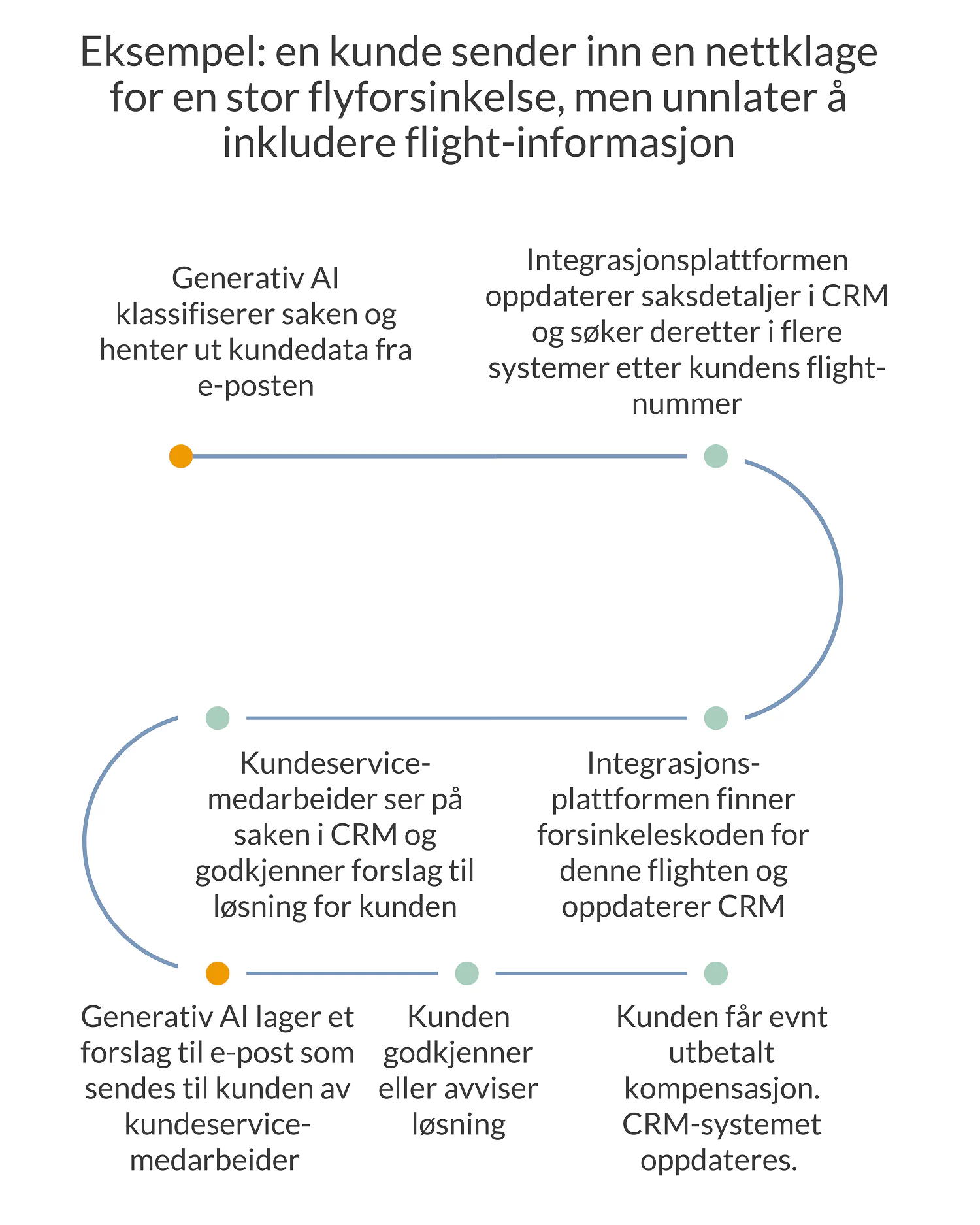
In other words, you should map out the process you want to improve, gain insights from the stakeholders and customers about what works well and what the “pain points” are, and then assess what change is required. Technology and sometimes generative AI can, as shown in the example, play a major role. But not always.
The hard part is not the technology
All the major players in data platforms have released solutions that make setting up these capabilities relatively easy. Examples include Databricks Mosaic and Snowflake Cortex.
As always, the biggest challenges to achieving impact are a) us humans, including being sufficiently clear about purpose and goals, b) changes that must be managed for each individual and c) not least the extent to which we have control of the data itself.
Want to learn more?
DigDir has developed a guide for responsible use and development of artificial intelligence, which is equally relevant in the private and public sector. NAV has also developed a guide, specifically for generative AI. Digital Norway produces good introductions to various topics, including artificial intelligence.
Feel free to also listen to the podcast “Datautforskerne”, episode 6, where Kjetil Åmdal-Sævik and Magne Bakkeli discuss generative AI, even though they themselves claim to be tired of talking about it. The episode is available on Spotify, Apple and Acast.
Like and subscribe!

