Database | What is a Database?
28.08.2022 | 3 min ReadTag: #database
A database is designed to store data. Databases are a common component in a great many IT solutions, because how else would we be able to keep track of all the transactions being made?
Databases store data in a structured manner
In a database, data is stored in tables and columns. A common database type is the relational database, where tables have relationships with each other through keys. One table contains, for example, information about customers, and another contains all the orders customers have placed.
A relational database uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to organise and make data searchable in table structures that are linked together with related information. Relational databases also possess other useful properties – for example, they are good at handling changes in data.
The most common use in a data and reporting context is that someone places a reporting tool such as Power BI directly on the database where the data is originally created – for example, the CRM system. Other times, we create a new database in order to retain more history than the source system itself stores on an ongoing basis. A standard relational database is in many cases sufficient for storing and retrieving data for simple user stories related to reporting and analytics, and is relatively straightforward to set up.
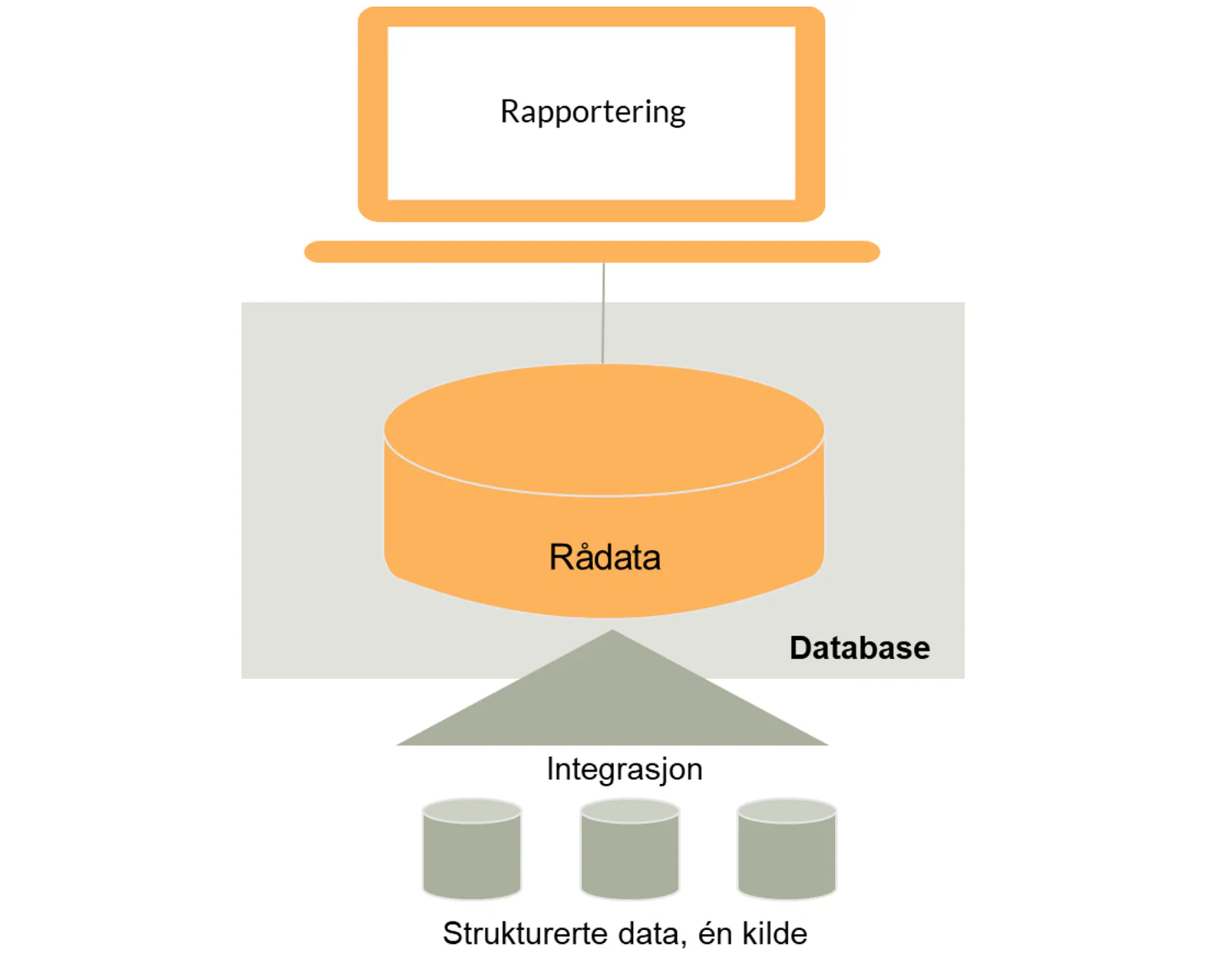
A database provides limited flexibility
The limitation lies in the fact that data remains as it was originally stored, meaning it is raw data that we actually want to process further so that it becomes easier to extract meaning from. Especially when we need to combine data from multiple sources, a conventional database structure can fall short.
We want to avoid data silos where we only have data about one thing at a time. We often need more functionality to transform and store data so that, for example, concepts such as customer and order can be analysed across sources, with consistency over time. In such cases, other forms of data storage may be more appropriate.
Advantages and disadvantages of databases
Below we summarise some important advantages and disadvantages of using the database of a source system (such as the HR system) directly as a basis for reporting and analytics:
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|

