
Databricks | A Guide
01.05.2023 | 8 min ReadWith the right data strategy, data organization, and architecture, businesses can gain insights that provide a competitive advantage. You also need technology. In this article, we discuss a major - and rapidly growing - SaaS technology, Databricks. We go through exactly what Databricks is and how the technology supports a data lakehouse architecture. We provide expert tips on how it should be used for data engineering or machine learning, and cover what sets Databricks apart from other tools that offer similar capabilities. We also provide resources to help you get started.
Contents
What is Databricks?
Databricks, developed by the creators of Apache Spark, is a cloud-based platform for data processing for analytics and reporting. The platform can transform data into insights using SparkSQL, provide active API connections to reporting tools such as Power BI, Qlikview, and Tableau, and build predictive models using SparkML.
Databricks runs on Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), making it easy for businesses to handle enormous amounts of data and perform machine learning tasks.
Databricks reduces the complexities of data processing for data scientists and data engineers, allowing them to develop ML applications using R, Scala, Python, or SQL interfaces in Apache Spark.
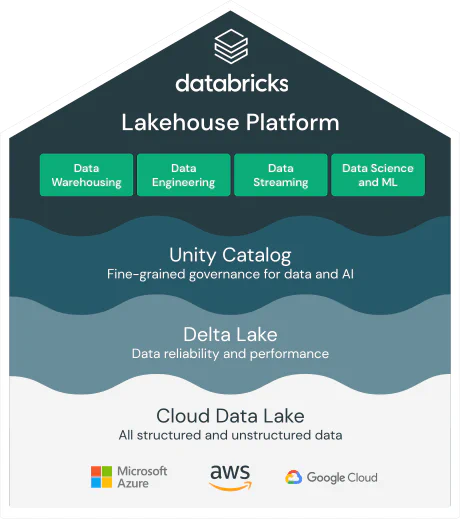
How does Databricks support a data lakehouse architecture?
Many businesses have until now collected large amounts of data either in data warehouses or data lakes. Databricks technology enables a data lakehouse architecture by combining the best features of both data lakes and data warehouses. A data lakehouse is a new type of data architecture that offers the benefits of data lakes (scalability, low cost, and flexibility) and data warehouses (performance, reliability, and structured data).
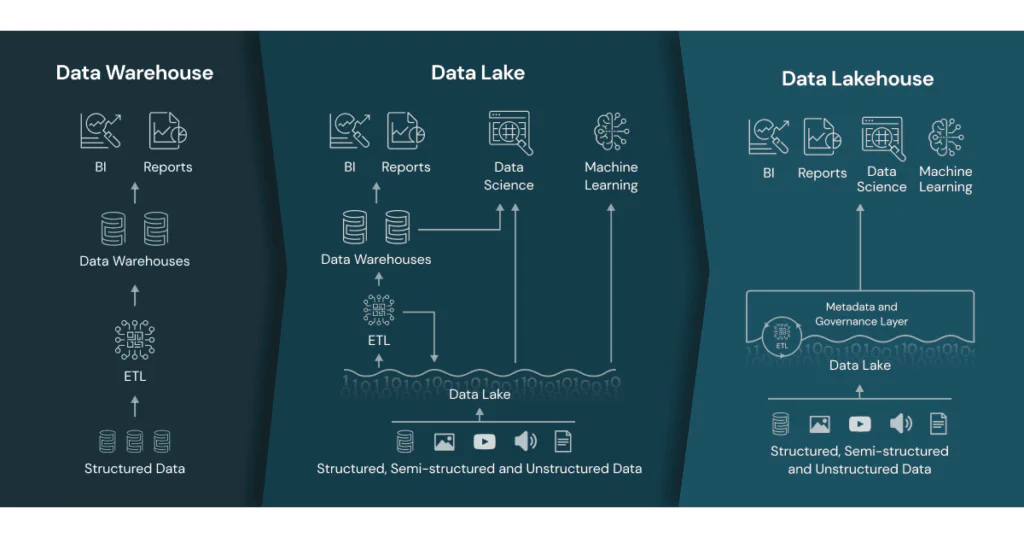
We believe Databricks supports the data lakehouse architecture through the following characteristics and features:
- Databricks introduced Delta Lake, a storage format that adds reliability and performance to data lakes. Delta Lake provides transactional consistency and version control through an ACID transaction engine. This helps solve some of the most common challenges associated with data lakes, such as handling unstructured data and ensuring reliability.
- Databricks leverages Apache Spark, an open-source distributed data processing engine, to offer scalability and high performance. Databricks has several built-in optimizations, such as Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) and Delta Engine, which improve performance by automatically optimizing queries. This means the data lakehouse architecture can scale to handle large amounts of data and perform complex analyses quickly.
- Databricks has built-in features to support the development and deployment of machine learning and AI models, while also supporting interfaces with common reporting tools such as Power BI, Tableau, and Qlik.
- Databricks supports a wide range of data sources and integrations, allowing businesses to collect and consolidate data from various sources in the data lakehouse architecture. The platform supports both batch and streaming data. Databricks can read and write data from/to various data formats such as Delta Lake, CSV, JSON, XML, Parquet, and others.
Databricks was the company that first introduced the data lakehouse concept. Note that other processing engines can also be used to enable such an architecture.
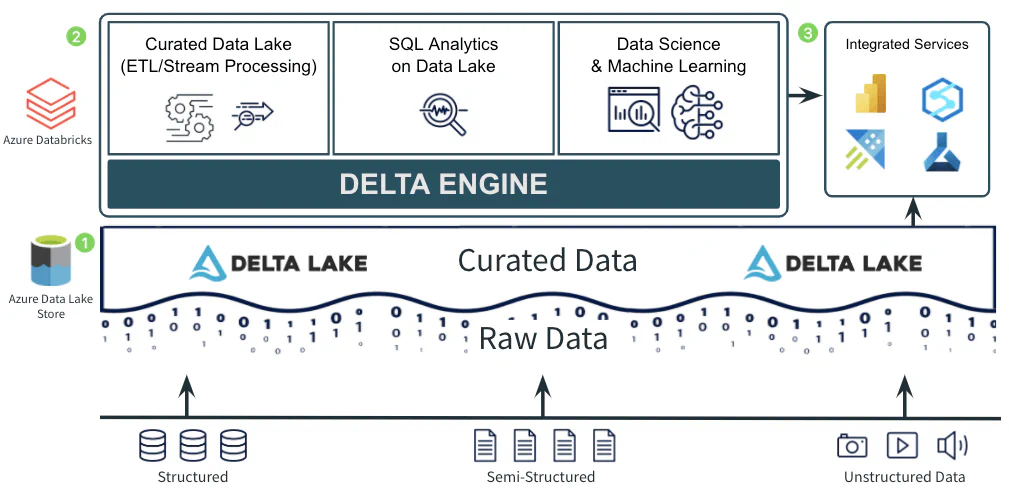
How does Databricks position itself against other tools?
There are many technologies that do a great job in data processing. Our experience is that the choice of technology depends on the existing needs and competencies within the organization.
We have highlighted some points that may be worth considering against your organization’s needs:
- Databricks only provides processing, not storage. Databricks is primarily aimed at being an efficient processing engine for code and algorithms. Databricks is, relative to some other processing engines, quite cost-effective. This will of course depend on which workloads are to be run.
- Databricks’ core architecture runs on Apache Spark, an open-source analytics engine focused on data parallelism. The Spark architecture works with a driver/worker node system, which lets you use many servers as one. Any number of worker/executor nodes work on the same job, piece by piece, and when each server is finished, it brings its output back to the main server/driver node and assembles everything for final output.
- Since Databricks is based on Open Source, many other open-source libraries such as Koalas can be used (similar to Pandas, but distributed on Apache). Data scientists can then use common packages such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, or scikit-learn.
- Databricks works on many cloud platforms and with many databases, providing good portability and reducing vendor lock-in. Databricks can run on Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Databricks is easy to get started with. Data engineers and data scientists can write code in their preferred language - SQL, Python, Scala, or R. Databricks’ notebook interface makes it relatively easy to collaborate with other developers on the same code. Pair programming and debugging become more efficient. Databricks can also be used to synchronize with GitHub, DevOps, or other code repositories.
Some advice from our experienced data engineers before implementing Databricks
We have described a comprehensive platform for data engineering and machine learning that is built to scale in the cloud and is well suited for medium-sized and large enterprises. If you are considering Databricks as a core solution for processing data, you should consider the following before making a decision:
- Do the basics first: Don’t be tempted by machine learning right away. Start by establishing one or more well-defined curated layers with descriptive metadata. If you can’t tell exactly what your sales figures are and where to find them, you shouldn’t be using a machine learning algorithm to predict future sales. Focus on the operational value of descriptive data before moving on to more complex features.
- Design an efficient and tidy data flow: Data should flow in one direction; otherwise, it can be challenging to maintain control over data origin and transformation. Define guidelines and data architecture that ensure you get a data lakehouse and not a data swamp.
- Clarify the conductor of the orchestra: How can you be sure that the data science team starts their jobs in sync with the completion of data engineering jobs? Understand how your Databricks scripts will be orchestrated and potentially use an external tool to coordinate all Databricks jobs. Establish processes and organization around this.
- Renew your competencies: Databricks is not a GUI-driven software. Data engineers and data scientists will write code that is unique to your use cases. Do you have the internal expertise to use Databricks properly? Are your data engineers able to write clean and efficient code? Where should this code be written? Do you have documentation in place during the transition to a new architecture? Investments in your data organization are always necessary to get value from investments in technology. Invest in talent and Databricks - it’s not either/or.
Frequently asked questions about Databricks
How does Databricks work with Apache Spark?
Databricks is tightly integrated with Apache Spark, a popular framework for large-scale data processing. The platform provides a simple way to create and manage Spark clusters and gives data engineers a user-friendly interface for writing and running Spark jobs. Databricks also provides auto-scaling, performance optimization, and error handling compared to standard Spark.
What is Databricks Runtime?
Databricks Runtime is a distributed data processing environment optimized for the Databricks platform. It includes built-in libraries specifically designed to work with large datasets and run complex analyses.
What is Delta Lake, and how does it work with Databricks?
Delta Lake is a storage system for large datasets developed by Databricks. Delta Lake is based on Apache Parquet and offers a range of features, including ACID transactions, time travel, and a data catalog.
How does Databricks work with SQL?
Databricks provides full support for both SQL and Python. This makes it easy for data engineers to run SQL queries and analyze data, while also providing excellent capabilities for data scientists to use Python functions and libraries.
What is Databricks Delta Live Tables (DLT)?
Databricks Delta Live Tables (DLT) is a feature in Databricks that helps data engineers and data scientists simplify and automate the building and maintenance of data pipelines in streaming and batch. DLT allows users to define data flows using SQL or Python.
What is Databricks Unity Catalog?
Databricks Unity Catalog is a centralized data catalog service that provides users of the Databricks platform with a unified view of all data assets and metadata across the organization. Unity Catalog simplifies data search, data discovery, and data governance, and features centralized access control across environments, data lineage, and a shared overview of data and resources.
What is MLflow?
MLflow is an open-source project developed by Databricks that aims to simplify the machine learning workflow. It provides data engineers and data scientists with a framework for tracking experiments, packaging and distributing models, and managing the machine learning process end to end.
Getting started with Databricks
- Databricks Community Edition: The best place to start is by creating a free Databricks community account. This will let you start a small cluster to experiment and get familiar with the basics of Databricks. It’s great to explore Databricks on your own, but we recommend using this alongside some form of online course (see below).
- Databricks Academy: The best resource we’ve found for learning Databricks is Databricks Academy. These courses are put together by Databricks themselves and are designed to get you ready to use Databricks for your use cases. Note that while there are some free courses, much of the training is relatively expensive.
- Databricks Community: This is a great resource for seeing what other users are doing with Databricks, and can be an excellent first place to go with any technical questions.
- Databricks Data Engineering Blog: Databricks’ own blog has a wealth of solutions posted for how to get the most out of Databricks.
- Free YouTube Databricks Overview: This video by Adam Marczak provides a concise summary of how to get started with Databricks.

