
Google BigQuery | A Guide
01.05.2023 | 9 min ReadIn this article, we discuss a major - and rapidly growing - SaaS technology, Google BigQuery. We go through exactly what Google BigQuery is and how the technology supports a data platform architecture. We also answer some common questions related to Google BigQuery and comparable solutions. We provide expert tips on how Google BigQuery should be used for data engineering and machine learning. We also provide resources to help you get started.
Contents
What is Google BigQuery?
Google BigQuery is a powerful, fully managed, serverless data storage and data warehouse solution provided by Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Google BigQuery is designed to handle enormous volumes of data and is particularly useful for running complex queries and analyses on large datasets in real time.
BigQuery is especially well known for its ability to scale seamlessly on demand, allowing organisations to store and analyse petabytes of data without having to worry about infrastructure and capacity.
Google BigQuery is deeply integrated into the Google Cloud platform, which means it can easily be combined with other Google Cloud services for even more powerful data analytics workflows. It uses SQL as its query language and is compatible with many existing data tools and libraries.
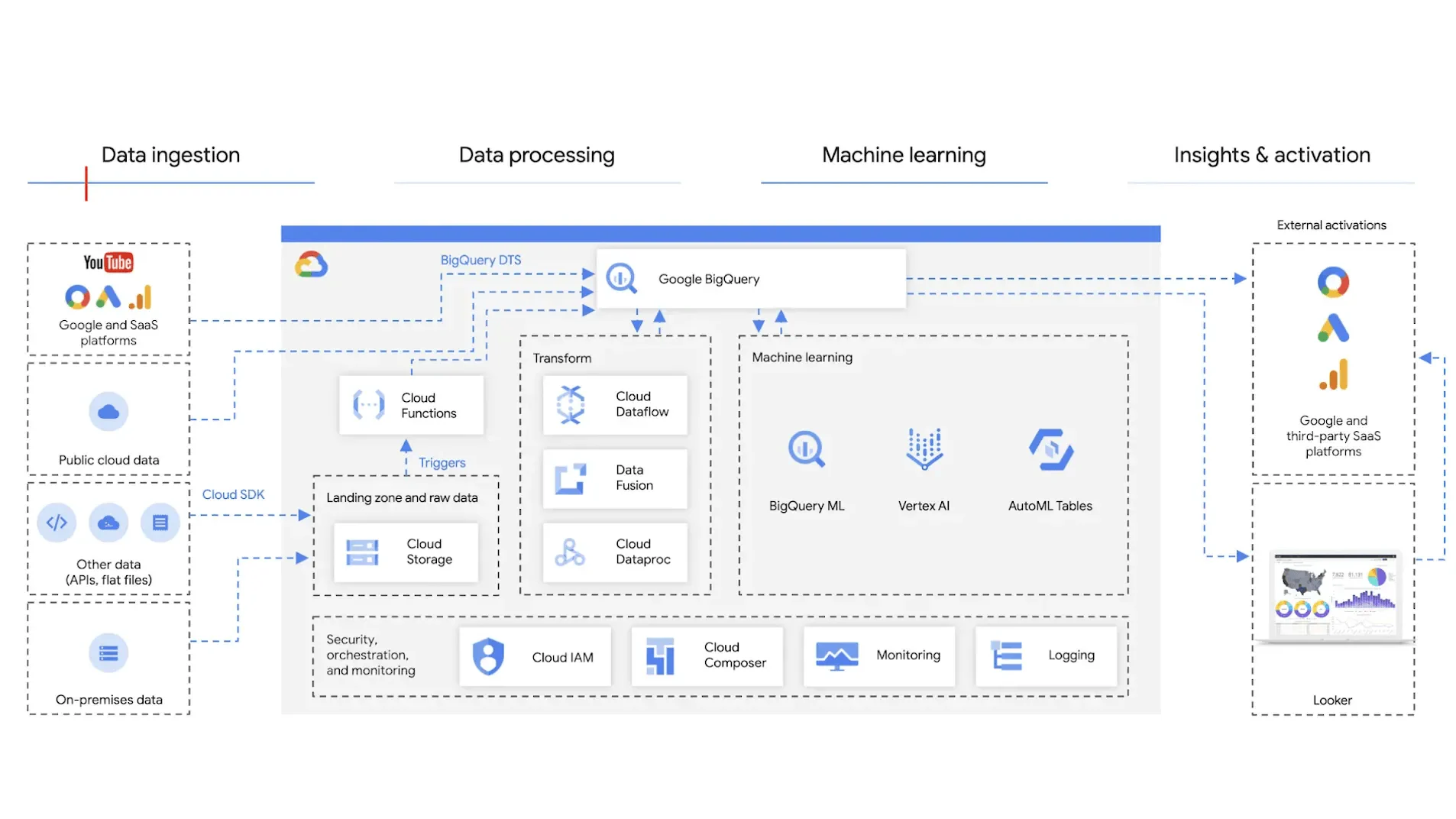
How does Google BigQuery fit into a modern data architecture?
Google BigQuery can play a central role as part of a data lakehouse architecture, an approach that combines the benefits of both data lakes and data warehouses.
In a data lakehouse architecture, BigQuery supports the following aspects:
- Data catalogue: BigQuery provides a centralised data catalogue where you can create, store, and manage datasets and tables. This helps organise data and promotes the reuse of datasets.
- Scalability: BigQuery is built on Google Cloud Platform and leverages its underlying services to handle large volumes of data, regardless of whether it is structured or unstructured.
- Data integration: BigQuery supports both batch and real-time data integration. For batch data, you can use integrations with data flows, data extraction, and data pipelines, such as Apache Beam, Dataflow, and Apache Airflow. For real-time data, you can use streaming APIs and services like Cloud Pub/Sub and Datastream.
- Machine learning: BigQuery ML allows you to build and deploy machine learning models directly within BigQuery using SQL, making it straightforward to perform predictive analytics.
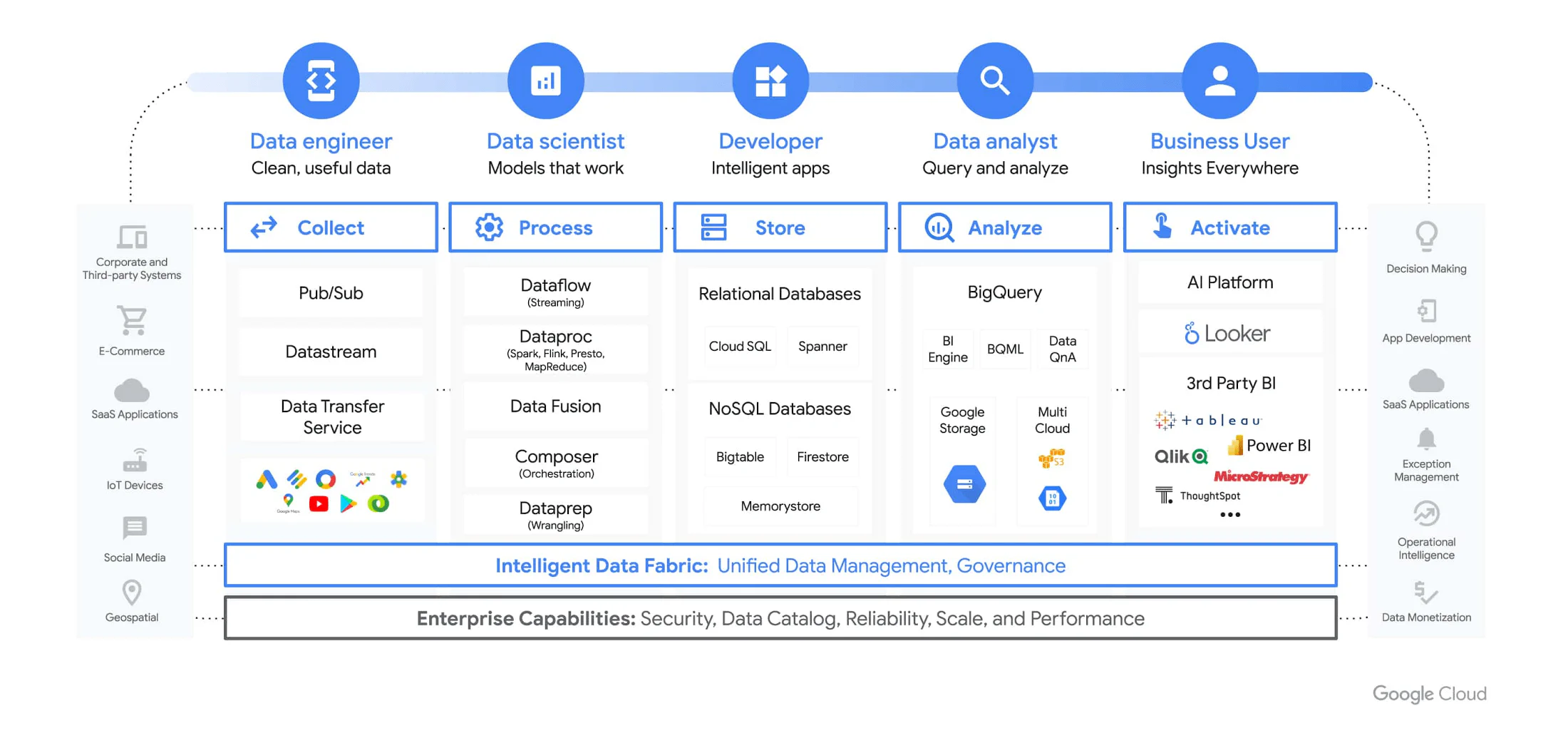
How does Google BigQuery position itself against other tools?
There are many technologies that do an excellent job in data storage and data processing. If your organisation already uses Google Cloud, BigQuery should be considered, as the Google ecosystem is well integrated and the database engine is very powerful. If Google Cloud is not already in use, there are several other good alternatives. Our experience is that the choice of technology depends on the existing needs and competencies within the organisation.
We have highlighted some points that may be worth considering against your organisation’s needs:
- Scalability and performance: Google BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless data warehouse service that provides excellent scalability and performance. It can handle petabyte-scale data analytics without the need to manage infrastructure, giving it an advantage over other tools that require significantly more resource management and performance optimisation.
- SQL support and integration: BigQuery supports standard SQL, making it straightforward for data engineers to use and integrate with existing data pipelines. This sets it apart from some other tools that require proprietary query languages or have limited SQL support.
- Machine learning capabilities: BigQuery ML gives data engineers and data scientists the ability to create and use machine learning models directly within BigQuery using SQL. This makes it easier to implement advanced analytical capabilities compared to other tools that may require external integrations or more complex workflows.
- Cost-effectiveness: BigQuery has an attractive usage-based pricing model, including storage and query costs. This makes it easy for data engineers to scale usage as needed and control costs more effectively. In addition, Google offers a range of discounts and savings based on long-term storage and usage. Generally, Google is often more affordable than comparable services on Azure and AWS.
- Ecosystem - but also vendor lock-in: BigQuery is part of Google’s cloud services, which means it is easy to integrate with other Google Cloud Platform services, such as Dataflow, Dataproc, and Google Data Studio. This provides a relatively seamless ecosystem for data engineers working with different aspects of data management and analytics. Note, however, that Google BigQuery is part of Google Cloud Platform and works best with other Google services. This can create a degree of vendor lock-in, compared to, for example, Databricks or Snowflake.
Some advice from our experienced data engineers before implementing Google BigQuery
We have described a comprehensive platform for data engineering and machine learning that is built to scale in the cloud and is well suited for medium-sized and large enterprises. If you are considering Google BigQuery as a core solution for processing data, here are five key points to consider before you start:
- Prepare for BigQuery-specific features: Google BigQuery has unique features and characteristics compared to other data warehouse solutions. It is important to familiarise yourself with these specific features, such as partitioned and clustered tables, materialised views, and the serverless architecture. Understand how these features can be used to your advantage to improve performance and reduce costs.
- Get to know the BigQuery SQL dialect: Although BigQuery uses SQL, it has its own SQL dialect with some peculiarities and features that may differ from other SQL dialects you may be accustomed to. Familiarise yourself with BigQuery-specific features such as ARRAY, STRUCT, and scripting to make the most of BigQuery.
- Optimise queries to reduce costs: In Google BigQuery, query costs are linked to the amount of data processed. Learn how to write efficient queries and use features such as filter pushdown, partitioning, and clustering to reduce the amount of data processed, thereby lowering costs.
- Leverage integration capabilities: BigQuery offers a wide range of integration options with other Google Cloud services and third-party tools for data collection, processing, analysis, and visualisation. Explore and leverage these integrations to build a robust and scalable data infrastructure around BigQuery.
- Use monitoring and alerting actively: Google Cloud Platform gives you access to tools such as Stackdriver Monitoring and Stackdriver Logging to monitor BigQuery service performance and logs. Learn how to use these tools to identify bottlenecks, performance issues, and potential errors, and set up alerts to be notified of important events and changes in resource usage.
Frequently asked questions about Google BigQuery
What sets Google BigQuery apart from other databases?
Google BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless, and scalable data warehouse solution offered by Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It is specifically designed to handle large volumes of data and is optimised for analytical purposes. BigQuery uses SQL syntax and sets itself apart from other databases by offering a serverless architecture, automated scaling, high performance, and seamless integration with other Google Cloud services.
How does the pricing for Google BigQuery work?
Google BigQuery has flexible pricing based on two models: On-Demand and Flat-Rate. On-Demand pricing charges you based on the volume of data you process, whilst Flat-Rate pricing offers a monthly price for unlimited usage. Costs include storage, streaming, and queries, and prices vary depending on region and performance requirements.
How can I transfer data to Google BigQuery?
To transfer data to BigQuery, you can use the Data Transfer Service (DTS) or third-party tools such as Apache NiFi and Talend. You can also build your own ETL pipelines using Google Cloud services such as Dataflow and Pub/Sub.
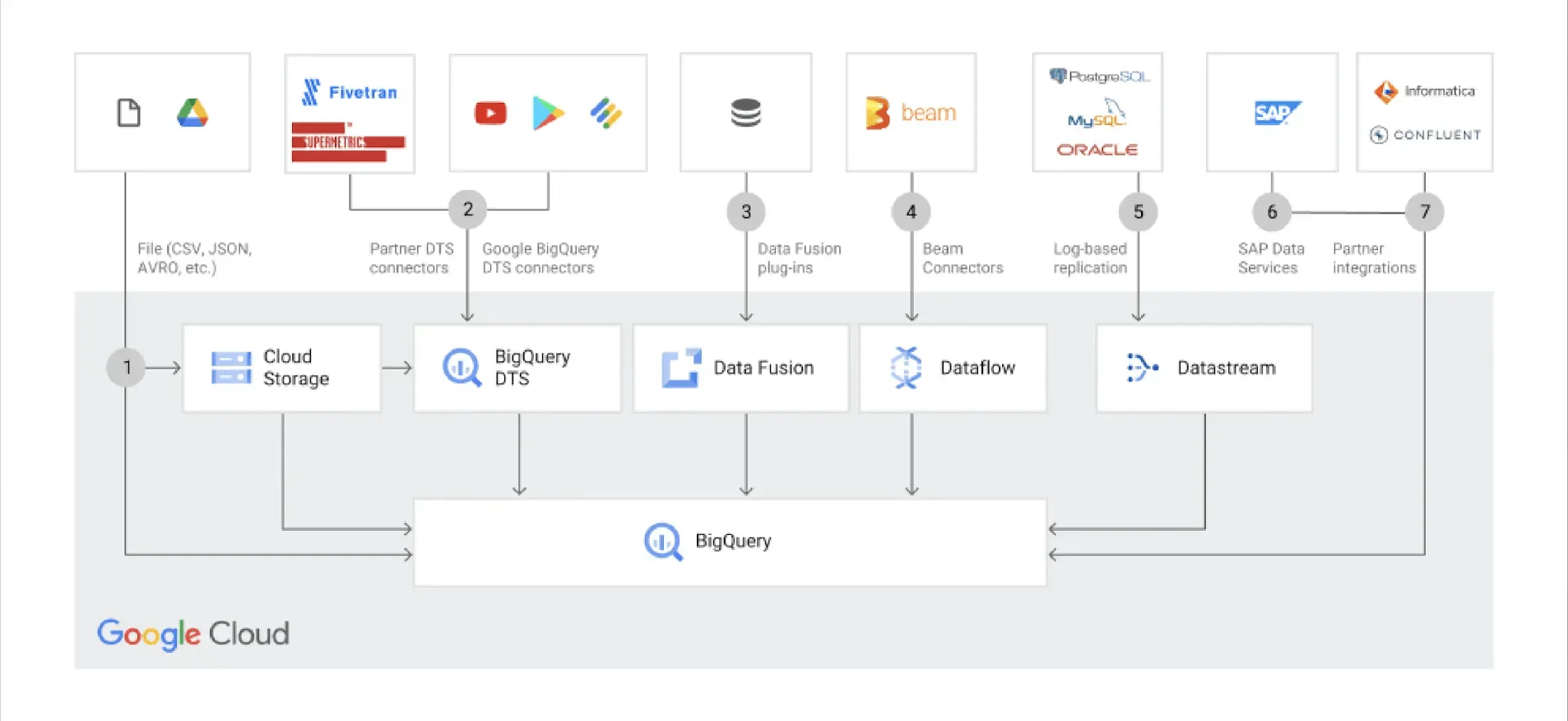
Is it possible to integrate Google BigQuery with other data analytics tools?
Yes, Google BigQuery supports integration with a range of popular data analytics tools such as Tableau, Looker, Data Studio, and Power BI. You can also use APIs and client libraries to integrate BigQuery with custom applications and services.
How does security work in Google BigQuery?
Google BigQuery provides security at multiple levels, including data encryption, network security, and user access control. Data stored in BigQuery is encrypted by default, both at rest and in transit. Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows you to control access to BigQuery resources and data in a granular manner.
How can I optimise query performance in Google BigQuery?
To optimise query performance in BigQuery, you should consider using partitions and clusters, writing efficient SQL queries, and using materialised views to reduce computational requirements. You can also monitor and analyse query performance using BigQuery Query Plan and BigQuery Job Information.
How can I store data in Google BigQuery cost-effectively?
To store data cost-effectively in BigQuery, you can use partitioning and clustering, which reduce storage costs and improve query performance. You can also leverage storage classes such as Long-Term Storage and Coldline Storage to minimise storage costs for infrequently accessed data. In addition, you can set up lifecycle rules to automate deletion or migration of old data to more affordable storage classes.
How can I manage and monitor Google BigQuery resources effectively?
To manage and monitor BigQuery resources effectively, you can use the Google Cloud Console, which provides a centralised platform for managing projects, datasets, tables, and jobs. You can also use Stackdriver Monitoring and Stackdriver Logging to monitor BigQuery service performance and logs. Furthermore, you can set up alerts to receive immediate updates on important events and changes in resource usage.
Getting started with Google BigQuery
To get started with Google BigQuery for testing and demonstrating its capabilities, you can do the following:
- Sign up for an account: Visit Google (https://cloud.google.com/bigquery) and sign up for an account. Google gives new customers $300 in free credits, which allows you to carry out a thorough test.
- Create a project and dataset to organise your data.
- Upload data files. There are several ways to do this, depending on the source of your data:
- Upload from local files: You can upload data files from your computer using the BigQuery web interface or command-line tools such as the
bqcommand. - Upload from Google Cloud Storage: If your data is already stored in Google Cloud Storage, you can easily import it into BigQuery. This is particularly useful for large datasets.
- Streaming ingestion: If you want to stream data in real time to BigQuery, you can use the BigQuery Streaming API.
- Upload from local files: You can upload data files from your computer using the BigQuery web interface or command-line tools such as the
- Choose the right data format and define the schema for the table.
- Start data ingestion and monitor the process.
If you want to learn more about Google BigQuery, there are many resources available. Here are some recommendations:
- Google Cloud Training: Google offers a range of courses and certifications related to BigQuery and other Google Cloud services.
- Online course platforms such as Coursera and Udemy offer many different BigQuery courses. These are created by both industry experts and self-proclaimed BigQuery experts, and are available at all levels.
- “Google BigQuery: The Definitive Guide”: This book, written by Valliappa Lakshmanan and Jordan Tigani, provides a thorough introduction to BigQuery for those who want a structured yet comprehensive overview.
- Google Cloud’s BigQuery Documentation: This is a comprehensive resource covering everything from basic concepts to more advanced topics. The documentation can be a bit overwhelming at first, but it is an essential source of answers to everything you might wonder about once you have got started.
- YouTube has, as always, many good introductory videos that will help you understand the key concepts. Here is a series we found useful.

