
Microsoft Fabric | A Guide
31.03.2025 | 8 min ReadIn this article, we go through what Microsoft Fabric is, which components are included in the product, and how it can be used to support a modern data platform architecture. We then discuss how Fabric positions itself in the market compared to alternative products. We provide expert tips on how Fabric should be used for data engineering and machine learning. Finally, we point you towards some resources you can use to get started with Fabric.
Contents
What is Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric is an integrated, cloud-based SaaS platform that brings together several of Microsoft’s data services, including Azure Synapse Analytics, Power BI, and Azure Data Factory, into one comprehensive solution. The solution is therefore intended to serve multiple needs from many different stakeholders within the same platform; roles ranging from technically oriented data engineers all the way to business users and analysts should be able to benefit from the platform.
This platform is designed to simplify data processing and enhance analytical capabilities by offering a unified storage structure called OneLake, where data from many different sources can be integrated, such as resources from cloud providers like Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud.
Fabric offers tailored tools and interfaces (known as “workloads” or “experiences”) based on each user’s role:
Data Engineering: Provides tools for building data lakehouses and other infrastructure for large-scale data collection, processing, and provisioning, including Notebooks, Apache Spark Jobs, Data Pipelines, Environments, and API for GraphQL.
Data Science: Facilitates the development and operationalisation of AI and machine learning models, supporting the entire process from data integration to prediction and insight. Includes tools such as Notebooks, Environments, ML Models, Experiments, and Apache Spark Jobs.
Data Warehousing: Offers scalable SQL-based data storage capabilities, with open data formats under the hood, along with the ability to independently scale compute and storage resources for efficient handling of large datasets. Includes tools such as Warehouse, Notebooks, and Mirroring.
Real-Time Intelligence: Enables real-time data analysis from various streaming sources, offering a comprehensive solution for event-driven scenarios and data logs. Includes tools such as Activator, Eventstream, and Eventhouse.
Power BI: Integrated into Microsoft Fabric to provide powerful, interactive reports and dashboards, giving users the ability to visualise and share insights effectively.
These are supported by the following core components in Fabric, which underpin much of the product’s functionality:
OneLake: The central storage structure in Microsoft Fabric, enabling data from various sources to be stored in a unified format. OneLake supports open data formats such as Parquet and Delta, ensuring accessibility and usability across different tools and platforms.
Data Factory: The data integration and orchestration service within Microsoft Fabric, based on Azure Data Factory. The tool supports a range of built-in connectors to various data sources, including databases, REST APIs, SaaS applications, and file systems, providing broad connectivity options for organisations.
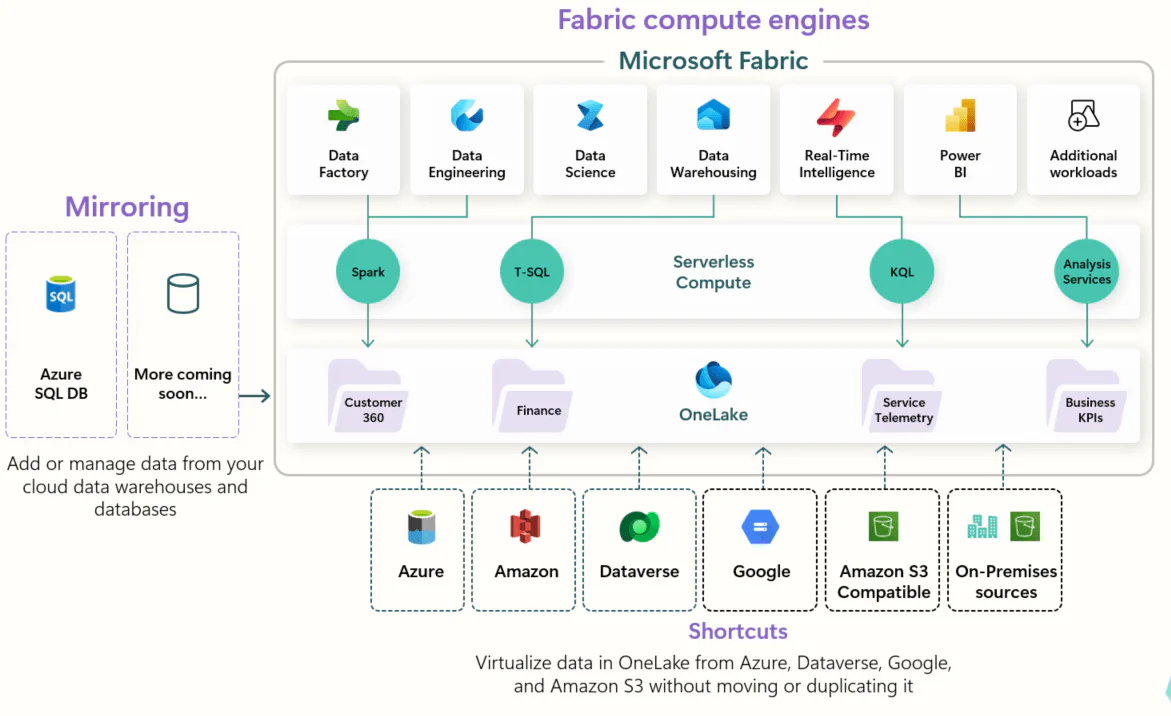
How does Microsoft Fabric fit into a modern data architecture?
Microsoft Fabric offers services that cover multiple needs for different use cases and stakeholders.
Unification of capabilities: In their communication around Fabric, Microsoft uses words such as “unification”, “integrated”, “seamless”, and “user-friendly”, which makes clear their goal for the platform to suit everyone who works with data in an organisation. The platform is “enterprise-ready” and supports the entire data process end to end. Microsoft’s goal is one platform for all. This includes data integration, data warehousing, advanced analytics, centralised storage in open file formats, data governance, different interfaces for different users, and centralised administration of users and other artefacts.
Easy to get started: Since Fabric is SaaS, it is very easy to get started. If you already have Power BI, you have access to Fabric as well! It is essentially a matter of creating a user account in Fabric, and then you can start building data products. There is no need to worry about spinning up separate cloud infrastructure.
Integration with other systems: Although Fabric is intended to be a single platform covering all needs, you still have the option to combine tools based on your requirements. Do you prefer a different tool for orchestration? Or for data science and advanced analytics? Then you can easily integrate these with Fabric and OneLake, so you can still choose tools based on your circumstances, experience, and preferences. Additionally, Fabric offers features such as Mirroring and Shortcuts, meaning you do not always need to integrate data from other areas - you can avoid the cost associated with duplicating and moving data into OneLake.
How does Microsoft Fabric position itself against other tools?
Microsoft Fabric can be a strong alternative for organisations that already use Microsoft services, for example through Azure:
Familiar technology: Since Fabric is based on well-known and widely used products such as Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Data Factory, Azure Storage, and Power BI, much will feel familiar to those already using Microsoft products. They are continuously developing more functionality, but the foundation is very similar. Since Fabric is SaaS, there is also an increased risk of vendor lock-in to an even greater extent than with Azure services - a risk that is somewhat lower with Databricks and Snowflake.
Future-oriented: It is clear that Microsoft is investing in Fabric as its new flagship within data and analytics, a role that Azure Synapse Analytics held until recently. This may be worth considering if you want to build a platform on Microsoft products today, as they are continuously releasing new and improved functionality. Microsoft Fabric will become increasingly seamless, tested, well-functioning, and modern as time goes on and more customers adopt the product.
Predictable and simple pricing model: Where services such as Azure Synapse Analytics, Databricks, and Snowflake largely have consumption-based pricing models, meaning you pay for processing time and capacity, Fabric has a capacity-based pricing model. This means you choose a capacity in advance, known as a Fabric Capacity SKU, from a list of options, similar to Power BI previously. Your choice of SKU determines how much processing power you have access to. Most features in Fabric are included in this pricing model, apart from some services such as OneLake storage, Power BI, and data integration, making it highly predictable and straightforward. You can change your SKU over time based on observed usage by following their pay-as-you-go model, or you can commit to a particular SKU over a set period, which unlocks a discounted total price if you know exactly what your needs are.
Some advice from our experienced data engineers before implementing Microsoft Fabric
- Plan the architecture carefully: Review and understand current and future user requirements that set the technical parameters. Also think early about volume, complexity, and the design of end-to-end data flows to evaluate components that suit the architecture.
- Assess needs and capabilities thoroughly: Ensure that Fabric contains the capabilities you are looking for. Are the data science capabilities sufficient? Are the data engineering capabilities sufficient? Do you have developers who are comfortable with the tools and frameworks offered? Such questions are, as always, just as important to answer when considering implementing Microsoft Fabric.
- Choose the right services for data integration and orchestration: Depending on technical needs, it is not necessary to use Data Flows, Data Pipelines, Mirroring, or Shortcuts. You can perfectly well choose other tools for data integration and orchestration, such as Azure Data Factory, if you want more flexibility. This may come at the expense of the relatively simple and predictable pricing model you get by staying within Fabric.
- Choose capacity according to need: Start with a low SKU and scale up if your computing requirements are not being met. Use Microsoft Fabric Monitor Hub and related platform services to keep track of cost drivers. Choose as low a SKU as possible without compromising productivity and performance.
- Security and monitoring: Ensure that you have designed for security in line with your organisation’s requirements and policies. This may include access control for services, networking, read access to data, and similar security requirements.
- Best practice: Established practices for lakehouse and data storage also apply to Microsoft Fabric. Start early by addressing low-hanging fruit that can save processing time and costs, such as sensible data integration processes, clearly defined data refresh frequencies, and logical division into table and folder structures.
- Choose tools carefully: Although Microsoft Fabric aims to be the be-all and end-all within data and analytics, we find that some of the services and products offered have gaps in functionality and that alternatives may provide more value and less frustration. Therefore, choose tools carefully, based on clear criteria relating to suitability, maturity, and robustness. There are also many good third-party solutions that integrate well with other Microsoft technologies.
Frequently asked questions about Microsoft Fabric
Which languages and frameworks does Microsoft Fabric support?
Microsoft Fabric supports several languages and frameworks, including T-SQL, KQL, Python, PySpark, Spark SQL, Scala, and R. This allows developers to use a range of familiar tools and languages.
How does the pricing for Microsoft Fabric work?
Pricing depends on which services you wish to use. Azure services for data and analytics often have both a consumption-based pricing model where you pay for processing time, and the option to lock in pricing by choosing dedicated resources if you have static processing requirements.
How does security work in Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric offers a single, comprehensive model for security and access control that comes enabled out of the box. The platform includes features such as encryption of data at rest in OneLake, secure network services, and firewall rules. When it comes to access control, each user must authenticate via Microsoft Entra ID, and all communication between users and the platform takes place over Microsoft’s closed and secured network. You can also add features such as Private Links and Entra Conditional Access. Finally, Fabric supports a range of compliance standards.
Getting started with Microsoft Fabric
If you want to learn more about Fabric, there are many resources available. Here are some recommendations:
- To get started with a free Fabric trial account, you can follow these steps from Microsoft.
- Microsoft offers a range of courses and certifications related to their services and products via Microsoft Learn, including Fabric. In addition, the documentation is often the best place to look for answers to both small and large questions about the platform.
- YouTube also has good introductory videos for understanding the key concepts. Here is a video we found useful:

